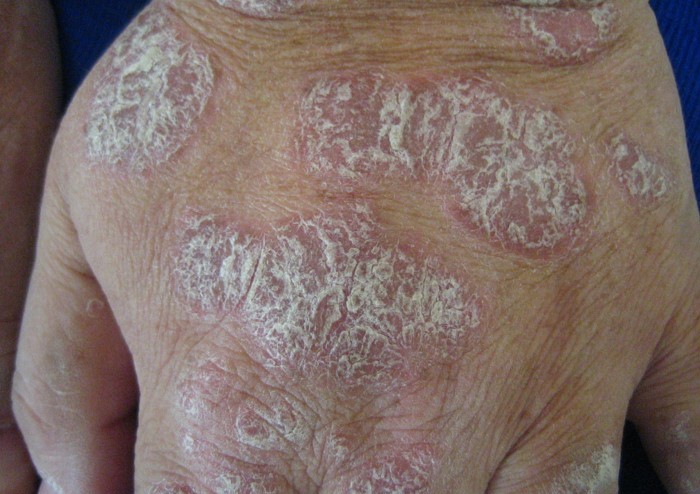
How Protein Peptides Help with Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that results in the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, scaly patches or plaques on the skin. These plaques are often itchy, red, and inflamed, and they commonly appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Psoriasis is considered a disease of the immune system, where the body’s immune cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, triggering the accelerated turnover of skin cells and leading to the buildup of plaques.
The condition can range from mild to severe, with some individuals experiencing only occasional flare-ups while others face more chronic and widespread symptoms. While there is no cure for psoriasis, treatments aim to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and slow down the overproduction of skin cells. Traditional treatments include topical creams, phototherapy, and systemic medications like biologics, which target the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Recent research has pointed to protein peptides as a promising new approach to treating plaque psoriasis. Peptides are short chains of amino acids that can interact with specific cellular pathways, offering more targeted and potentially more effective treatments. Certain protein peptides have shown the ability to regulate immune responses, reduce inflammation, and promote skin cell repair, making them a potential breakthrough in managing plaque psoriasis.
This article will explore how protein peptides can help treat plaque psoriasis, the mechanisms through which they work, and the potential benefits they offer in psoriasis management.
Understanding Plaque Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes the rapid turnover of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow and shed in a cycle that takes about 28 to 30 days. In individuals with psoriasis, this cycle is shortened, with skin cells growing and shedding in just a few days. This rapid turnover leads to a buildup of dead skin cells on the surface of the skin, forming thick, silvery plaques.
In plaque psoriasis, the immune system is overactive, specifically T cells, which are a type of white blood cell involved in immune response. In healthy individuals, T cells help protect the body from infections. However, in people with psoriasis, T cells mistakenly attack the skin cells, causing inflammation and stimulating the rapid turnover of skin cells. This immune dysregulation leads to the characteristic plaques associated with psoriasis.
The symptoms of plaque psoriasis can vary widely from person to person and may include:
- Raised, red patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning, or soreness in the affected areas
- Thickened or ridged nails
- Swollen or stiff joints (psoriatic arthritis)
Although psoriasis is not contagious, it can be triggered or exacerbated by environmental factors such as stress, infections, certain medications, or skin injury.
How Protein Peptides Can Help with Plaque Psoriasis
Protein peptides offer a novel approach to psoriasis treatment by targeting the immune system and skin regeneration processes. These peptides can interact with specific molecular pathways that regulate inflammation, immune cell activity, and skin cell turnover, potentially reducing the severity of psoriasis and promoting skin healing. Below are some of the key ways in which protein peptides can help treat plaque psoriasis.
1. Modulating the Immune Response
The primary driver of psoriasis is the dysregulated immune system, where T cells mistakenly attack healthy skin cells. Peptides that can modulate the immune system may offer a way to reduce the inflammation and immune activation that leads to the development of psoriasis plaques.
- Interleukin-10 (IL-10) Peptides: IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine that plays a key role in controlling immune responses. It helps regulate the production of other cytokines and suppresses the activation of T cells, which are involved in the inflammatory process of psoriasis. IL-10 peptides are being investigated for their ability to restore immune balance by suppressing the overactive immune responses seen in psoriasis. By promoting a more controlled immune response, IL-10 peptides may reduce inflammation and prevent the rapid turnover of skin cells.
- TNF-alpha Inhibitor Peptides: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is overexpressed in many inflammatory diseases, including psoriasis. TNF-alpha promotes the activation of immune cells and contributes to the development of skin plaques. Certain protein peptides are being developed to inhibit the action of TNF-alpha, which could help reduce the inflammation and skin cell turnover seen in plaque psoriasis.
2. Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is a hallmark of plaque psoriasis, and controlling this inflammation is crucial for managing the condition. Some peptides have anti-inflammatory properties that can directly target the inflammation in the skin and underlying tissues.
- BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound 157): BPC-157 is a synthetic peptide that has shown potent anti-inflammatory effects and is known for promoting tissue healing. Studies suggest that BPC-157 can reduce inflammation in various tissues, including the skin, and may help accelerate the healing of psoriasis plaques. By reducing local inflammation, BPC-157 could help alleviate the pain and redness associated with psoriasis flare-ups.
- Thymosin Beta-4 (TB-500): TB-500 is another peptide with anti-inflammatory properties. It has been shown to promote the healing of tissues by reducing inflammation and enhancing cell migration and collagen production. In the context of psoriasis, TB-500 may help reduce the swelling and redness associated with plaques while supporting tissue repair and regeneration.
3. Promoting Skin Regeneration and Healing
In addition to modulating immune responses and inflammation, protein peptides can also promote skin regeneration, which is key in treating plaque psoriasis. Since psoriasis is characterized by rapid skin cell turnover, promoting normal skin regeneration can help restore healthy skin and reduce the appearance of plaques.
- GHK-Cu (Copper Peptide): GHK-Cu is a naturally occurring peptide that has been extensively studied for its regenerative properties. It has been shown to stimulate collagen production, enhance wound healing, and reduce inflammation. Copper peptides like GHK-Cu can help promote the healing of psoriasis plaques by stimulating the production of collagen and other extracellular matrix components that are essential for skin repair. Additionally, GHK-Cu has antioxidant properties, which can protect skin cells from oxidative stress and promote healthier skin regeneration.
- Collagen Peptides: Collagen is an essential component of the skin’s structure, and collagen peptides are being studied for their ability to support skin regeneration and repair. By stimulating the production of collagen, collagen peptides can help improve the structural integrity of the skin, promote the healing of psoriasis plaques, and enhance overall skin health.
4. Enhancing Skin Barrier Function
The skin barrier in individuals with psoriasis is often compromised, making the skin more vulnerable to infections and irritants. Peptides that enhance skin barrier function can help protect the skin and prevent further flare-ups of psoriasis.
- Filaggrin-Mimicking Peptides: Filaggrin is a key protein involved in maintaining the skin’s barrier function. Individuals with psoriasis often have lower levels of filaggrin, which contributes to skin dryness and permeability. Peptides that mimic the effects of filaggrin could help improve the skin’s barrier function, reduce water loss, and enhance overall skin health, which may help manage psoriasis symptoms.
The Potential Benefits of Protein Peptides for Plaque Psoriasis
Protein peptides offer several potential benefits for individuals with plaque psoriasis:
- Targeted Action: Peptides can specifically target immune cells, inflammatory pathways, and skin regeneration processes, offering a more precise treatment compared to traditional therapies.
- Reduced Side Effects: Since peptides are smaller molecules, they may have fewer side effects compared to systemic immunosuppressive drugs and biologics.
- Enhanced Healing: Peptides like GHK-Cu and collagen peptides can promote skin regeneration and improve the healing of psoriasis plaques, helping to restore healthy skin.
- Long-Term Management: By addressing the underlying immune dysfunction and inflammation in psoriasis, peptide-based therapies may offer a more sustainable solution for managing the condition over the long term.
Challenges and Considerations
While peptide-based therapies for plaque psoriasis are promising, there are still challenges to overcome before they can become widely used in clinical practice. The effectiveness and safety of these peptides must be thoroughly tested in clinical trials to ensure they provide reliable and long-term benefits. Additionally, the delivery methods for peptides must be optimized to ensure they can reach the skin and exert their effects efficiently.
Conclusion
Protein peptides offer a novel and promising approach to treating plaque psoriasis by targeting the underlying immune dysfunction, reducing inflammation, promoting skin regeneration, and improving skin barrier function. Peptides like BPC-157, TB-500, GHK-Cu, and collagen peptides show potential in reducing the severity of psoriasis symptoms and promoting the healing of plaques. As research into peptide-based therapies for psoriasis continues, these peptides may become an important part of the treatment landscape, offering a more targeted, effective, and sustainable approach to managing this chronic condition.
- BPC‑157 & skin healing (animal model): “BPC 157… found to rapidly stimulate the expression of various genes involved in the healing process of the skin and mucosal lesions” (FASEB Journals).
- GHK‑Cu’s relevance to psoriasis and skin repair: “GHK‑Cu and other peptides used topically… Cur‑CNEs/Gel exhibits effective alleviation of the symptoms of psoriasis in mice and provides a promising strategy for topical treatment of psoriasis” (Longevity Protocols).
- IL‑10’s therapeutic potential in psoriasis: “IL‑10 administration represents a new therapeutic approach” in psoriasis (PMC).
- Thymosin β4’s anti‑inflammatory, regenerative properties: Demonstrated anti‑inflammatory activities in the skin (PMC).
- Collagen peptides & inflammation in psoriasis: Collagen may help reduce inflammation and improve skin elasticity in individuals with psoriasis (Healthline).
- Hydrolyzed collagen’s anti‑inflammatory and skin‑repair effects: It induces an anti‑inflammatory response and promotes proliferation of skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes (PMC).
Summary of Key Peptide Effects on Plaque Psoriasis
| Peptide / Mechanism | Evidence Highlight |
|---|---|
| BPC-157 | Stimulates gene activation tied to skin and mucosal healing in animal models. |
| GHK-Cu (Copper peptide) | Topically alleviates psoriasis-like symptoms in mice through skin regeneration. |
| IL-10 Peptides | Anti-inflammatory cytokine; therapeutic administration shown effective in psoriasis. |
| Thymosin β4 | Exhibits strong anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties in skin tissue. |
| Collagen Peptides | May reduce inflammation and improve skin elasticity in psoriasis sufferers. |
| Hydrolyzed Collagen | Enhances skin cell proliferation and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. |